 Tokyo Institute of Technology, Associate Prof. Takuya HARADA
Tokyo Institute of Technology, Associate Prof. Takuya HARADA
"Global warming", we have been hearing this term on the TV news for quite some time now. The average global temperature is rising, the Antarctic and Arctic ice sheets are melting, sea levels are rising, and we are being hit more frequently by severe typhoons and heat waves. Many studies and analyses around the world have shown that such serious global climate change is advancing. The substance responsible for global warming is carbon dioxide (CO2), which we humans are releasing into the atmosphere in large quantities, and the CO2-rich atmosphere is like a plastic greenhouse, trapping heat from the sun and raising the global temperature as a result.
Naturally, reducing atmospheric CO2 emissions is essential to halt this global warming process. There are two major technological approaches to this end. One is the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power and carbon-free energy sources such as nuclear power, and the other is technology to capture and reuse CO2 emitted from the consumption of fossil fuels. The latter technology is called CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage) or CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage) in particular, and its establishment is highly anticipated.
As one of the activities of Tokyo Tech GXI, our laboratory has been conducting research focusing on CO2 capture and reuse technology. In particular, we have been developing a new CO2 capture system using a unique material called "molten oxide" (Figure 1). Oxides are generally in solid form, such as ceramics and glass, but molten oxides are those that have been heated and melted to a liquid state.
We have developed a material with excellent CO2 reactivity and high thermal stability from among these molten oxides, and by using it as a new CO2 absorbent, we have realized a system that can directly capture CO2 from high-temperature combustion gases emitted from factories and thermal power plants. This new high-temperature-liquid CO2 recovery system can also efficiently convert the large amount of thermal energy generated by the CO2 reaction into electrical energy (i.e., "power generation"), resulting in a significant reduction in process energy consumption. This has led to a significant reduction in process energy consumption. Such simultaneous CO2 capture and heat recovery power generation would not have been possible with conventional CO2 absorbers that operate at low temperatures or with solid CO2 absorbers that have low thermal conductivity.
Reuse of recovered CO2 is another important technical issue. We are considering the reuse of CO2 as a new carbon resource that can replace petroleum as a raw material for synthesizing various chemical products such as polymers and chemical fuels. Our newly developed CO2 recovery method using molten oxides has a great technological advantage in terms of CO2 conversion and reuse, as it can easily extract CO2 to a high purity after recovery.
The problem of global warming is a major global issue that confronts us in this day and age. However, I believe that we can surely solve this problem if we all work as one and continue to make great efforts. Through the research of CO2 capture technology at Tokyo Tech GXI, I would like to accelerate our progress together with our many partners.
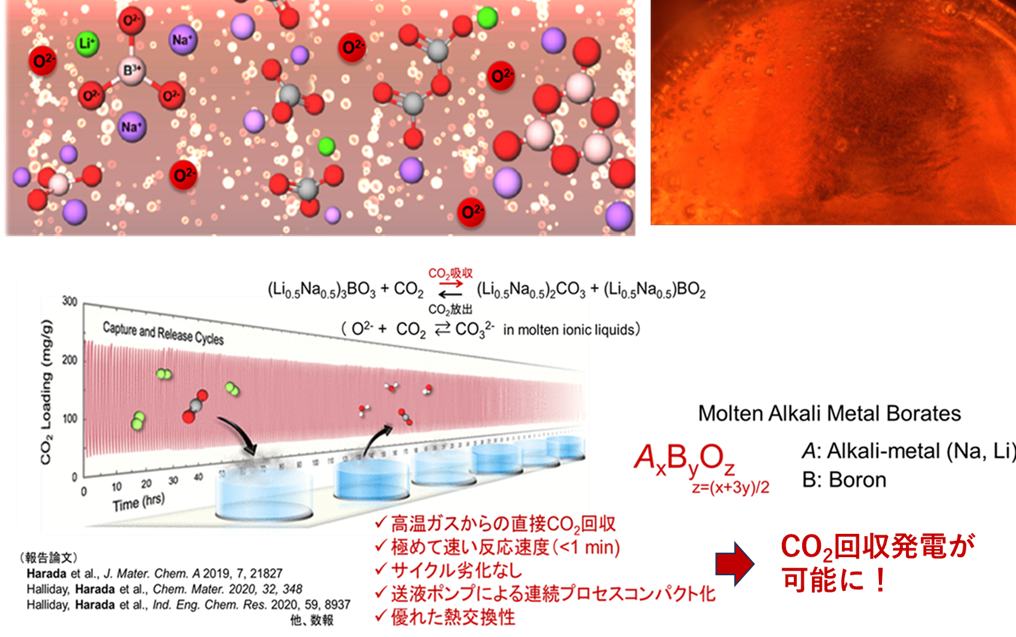 Figure1 Conceptual diagram and characteristics of a new molten oxide type CO2 absorber.
Figure1 Conceptual diagram and characteristics of a new molten oxide type CO2 absorber.


